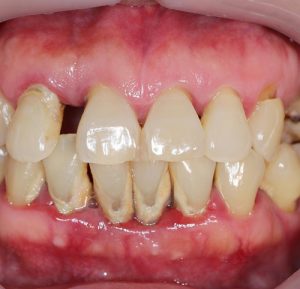
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common condition that affects the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth. It is primarily caused by bacteria in dental plaque, a sticky film that forms on the teeth. If left untreated, gum disease can lead to tooth loss and other serious oral health problems. Let’s explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for gum disease
Causes:
1. Poor oral hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to accumulate on the teeth and gums.
2. Smoking: Tobacco use is a significant risk factor for gum disease as it weakens the immune system and impairs gum tissue healing.
3. Hormonal changes: Hormonal fluctuations during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause can make gums more sensitive and prone to inflammation.
4. Diabetes: People with diabetes have a higher risk of developing gum disease due to reduced ability to fight infections.
5. Certain medications: Some medications, such as anticonvulsants and oral contraceptives, may increase the risk of gum disease.
6. Genetic factors: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to gum disease.
Symptoms:
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bleeding gums, especially during brushing or flossing
- Receding gums or a change in the gumline shape
- Persistent bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Changes in bite or the way the teeth fit together
Treatment options:
- Professional dental cleaning
“As a dentist, one of the most common concerns I come across in my patients is gum disease. Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common condition characterized by inflammation and infection of the gums. It can lead to a range of oral health problems, including tooth loss if left untreated. Fortunately, professional dental cleaning solutions can play a crucial role in managing and treating gum disease.” Dr. Jane
- Jane continues explaining; when patients come to me with signs of gum disease, such as red, swollen gums that bleed easily, I emphasize the importance of professional dental cleanings. While regular brushing and flossing are essential for maintaining good oral hygiene, they may not be enough to prevent or treat gum disease. Professional dental cleanings, also known as scaling and root planing or deep cleaning, are specialized treatments that go beyond regular brushing and flossing to target gum disease specifically.
- During a professional dental cleaning, I use special tools to remove plaque and tartar buildup from the teeth and along the gumline. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth, and if not removed, it can harden into tartar, which is more difficult to remove and can lead to gum inflammation. By removing plaque and tartar, a professional dental cleaning helps to eliminate the source of infection and reduces the risk of gum disease progression.
- Professional dental cleanings also involve a process called root planing, which smooths the tooth roots to remove rough spots and make it harder for bacteria to adhere to the teeth. This helps to promote gum reattachment and reduce the depth of periodontal pockets, which are spaces that form between the gums and teeth due to gum disease. By eliminating these pockets, the cleaning can prevent further bacterial accumulation and facilitate the healing process.
- In addition to the physical cleaning, professional dental cleanings provide an opportunity for dentists to educate patients about proper oral hygiene techniques and provide personalized recommendations. This may include demonstrating effective brushing and flossing techniques, recommending antimicrobial mouth rinses or other dental products, and discussing lifestyle factors that may contribute to gum disease, such as smoking or poor nutrition. By addressing these factors and providing individualized guidance, dentists can help patients improve their oral health and reduce the risk of gum disease recurrence.
- It’s important to note that professional dental cleanings are not a one-time solution for gum disease. Depending on the severity of the condition, multiple sessions may be necessary to effectively treat the disease. Furthermore, regular follow-up visits for maintenance cleanings are crucial to prevent the recurrence of gum disease and maintain optimal oral health.
- Medications:
At Gentle Dental Care we believe that it’s crucial to educate and advise patients about various treatment options for gum disease. Along with professional dental procedures, medications can play a significant role in managing and treating gum disease, also known as periodontal disease. Medications can be used as adjuncts to traditional dental treatments to enhance their effectiveness and control the progression of the disease.
Here are some common medication solutions that Dr. Jane may recommend to patients dealing with gum disease:
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are often prescribed to combat the bacterial infection responsible for gum disease. They can be administered orally or topically. Oral antibiotics like doxycycline, minocycline, and metronidazole may be prescribed in severe cases or as a short-term treatment. Topical antibiotics such as antimicrobial mouth rinses or gels containing chlorhexidine can also be recommended to control bacterial growth.
- Antiseptic Mouthwashes: Over-the-counter antiseptic mouthwashes containing ingredients like chlorhexidine or hydrogen peroxide can help reduce plaque and gingivitis. They can be used as a supplementary home care routine alongside regular brushing and flossing. However, it’s important to follow the instructions provided by the dentist or on the product label to avoid any side effects or misuse.
- Prescription Mouthwashes: In some cases, dentists may prescribe stronger antimicrobial mouth rinses to help control bacteria and reduce inflammation. These mouthwashes may contain a combination of antibiotics, antiseptics, or anti-inflammatory agents to target specific aspects of gum disease. It’s essential to use prescription mouthwashes as directed and for the recommended duration.
- Oral Antiseptics: Dentists may recommend oral antiseptic gels or solutions containing chlorhexidine, which can be applied directly to the gums using a cotton swab or a tray. These antiseptics can help reduce bacteria and control gum inflammation. It’s important to follow the dentist’s instructions regarding frequency and duration of use, as prolonged or excessive use may lead to tooth staining or other side effects.
- NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs): For patients experiencing discomfort or inflammation due to gum disease, dentists may recommend over-the-counter NSAIDs like ibuprofen to manage pain and reduce swelling. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional or follow the instructions provided by the dentist to ensure proper dosage and avoid any potential drug interactions or adverse effects.
- Surgery:
In advanced cases, surgical interventions such as flap surgery, bone grafts, or tissue grafts may be necessary to repair damaged gums and bone. Dr. Jane is committed to informing and advising her patients about the latest advancements in surgery solutions for gum disease. We explore these surgical options and their benefits in effectively treating gum disease.
- Pocket Reduction Surgery:
Also known as flap surgery or osseous surgery, pocket reduction surgery is a common surgical procedure used to treat moderate to advanced gum disease. The surgery involves lifting the gum tissue and accessing the underlying infected areas, allowing the dentist to thoroughly clean the root surfaces and remove tartar deposits. This procedure aims to reduce the depth of the gum pockets, making it easier for patients to maintain proper oral hygiene.
- Soft Tissue Grafts:
Gum disease can cause gum recession, leading to exposed tooth roots and an unsightly appearance. Soft tissue grafts are often recommended to repair receding gums and improve aesthetics. During the procedure, gum tissue is taken from another area of the mouth or a donor source and placed over the exposed roots. This helps to protect the tooth structure, prevent further recession, and restore a natural gumline.
- Bone Grafting:
Severe gum disease can result in bone loss around the teeth, compromising their stability. Bone grafting is a surgical solution that aims to regenerate lost bone tissue. The procedure involves placing bone graft material, either from your own body or a synthetic source, into the affected areas. Over time, the graft material stimulates new bone growth, restoring strength and stability to the teeth.
- Lifestyle changes:
While professional dental care is essential for managing gum disease, Dr. Jane also emphasizes the importance of lifestyle changes to prevent and improve the condition. Let’s see several lifestyle changes recommended by her to combat gum disease effectively.
- Oral Hygiene Practices:
- Maintaining proper oral hygiene is crucial for preventing and managing gum disease. Dr. Jane advises patients to follow these practices:
- Regular Brushing: Brush your teeth at least twice a day using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Pay close attention to the gum line, gently massaging the gums in a circular motion.
- Flossing: Clean between your teeth daily using dental floss or interdental brushes to remove plaque and debris that brushing alone cannot reach.
- Mouthwash: Rinse your mouth with an antimicrobial mouthwash recommended by your dentist. This helps reduce bacteria and controls plaque formation.
- Balanced Diet:
- A healthy diet plays a vital role in maintaining overall oral health, including gum health. We advise patients to make the following dietary changes:
- Limit Sugary Foods: Reduce the consumption of sugary snacks and beverages, as they promote bacterial growth and plaque formation, increasing the risk of gum disease.
- Increase Fruit and Vegetable Intake: Include a variety of fruits and vegetables in your diet, as they provide essential nutrients and antioxidants that support gum health.
- Adequate Water Intake: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stimulate saliva production, which helps in rinsing away bacteria and maintaining a healthy oral environment.
- Tobacco Cessation:
- Smoking and tobacco use are major risk factors for gum disease. At Gentle Dental Care, we strongly advise patients to quit smoking and other forms of tobacco use. Tobacco damages gum tissue, weakens the immune system, and hampers the body’s ability to fight infections. By quitting tobacco, patients can significantly reduce their risk of developing gum disease and improve their overall oral health.
- Stress Reduction:
- Stress can have detrimental effects on oral health, including an increased risk of gum disease. Dentists recommend stress management techniques, such as regular exercise, meditation, deep breathing exercises, and engaging in hobbies or activities that help reduce stress levels. By managing stress effectively, patients can minimize the impact on their oral health.
- Regular Dental Check-ups:
- Maintaining regular dental check-ups is crucial for the prevention and early detection of gum disease. We can identify any signs of gum disease at its early stages, provide professional cleaning, and offer personalized advice based on each patient’s oral health needs.
It’s important to note that prevention is key in maintaining healthy gums. Regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups, along with a healthy lifestyle, can significantly reduce the risk of gum disease. If you suspect you have gum disease or are experiencing any symptoms, it’s best to consult Gentle Dental Care Clinic for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.

